Cloud Computing Explained: Public vs. Private vs. Virtual Private
Let’s talk about cloud in simpler terms!
Coming across different terms about a technology without actually getting your head around what they meant is a common issue. Recently, I decided to study Cloud Computing and I wanted start by learning the terminology and then diving deeper into the specific topics.
With the first post of the “Cloud Computing Explained” series, we will look at a small but commonly used subset of cloud terms:
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Virtual Private Cloud
Let’s first look at the definitions, and then create an analogy to make them easy to remember!
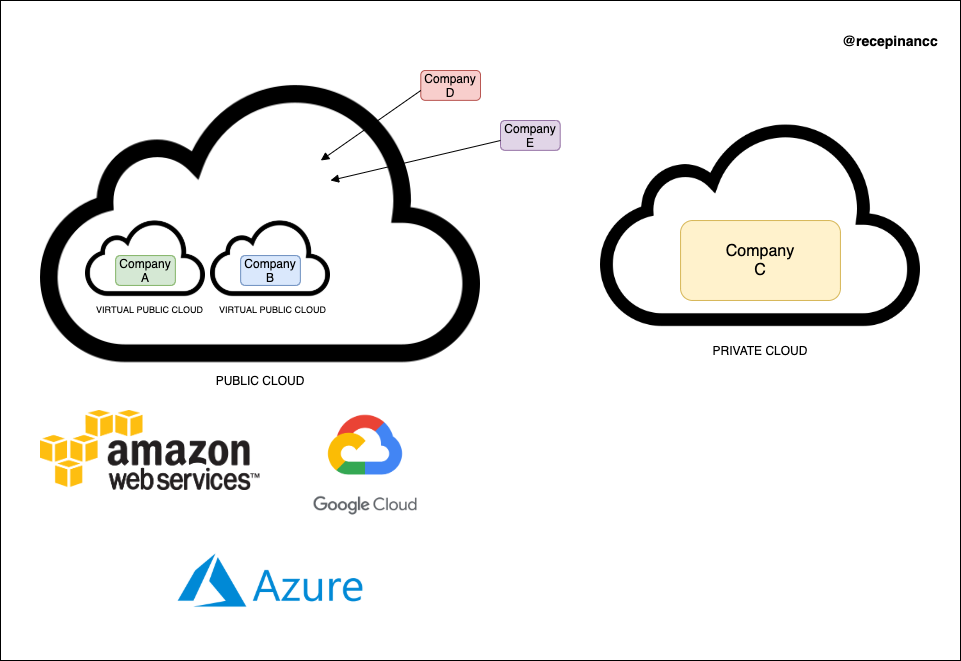
Public Cloud
A Public Cloud is a set of cloud services provided to you and other customers by a vendor.
The Public Cloud enables us to provision resources on-demand according to our needs. There are many different vendors for public cloud services that offer you variant solutions based on your needs to build your software.
As these solutions’ levels go down, it gives you more control over the resource. However, this also means more overhead since you’ll have more things to do for that resource to be working reliably.
And one of the tremendous benefits of the public cloud is that you only pay for what you use. That gives you the ability to optimize your expenses.
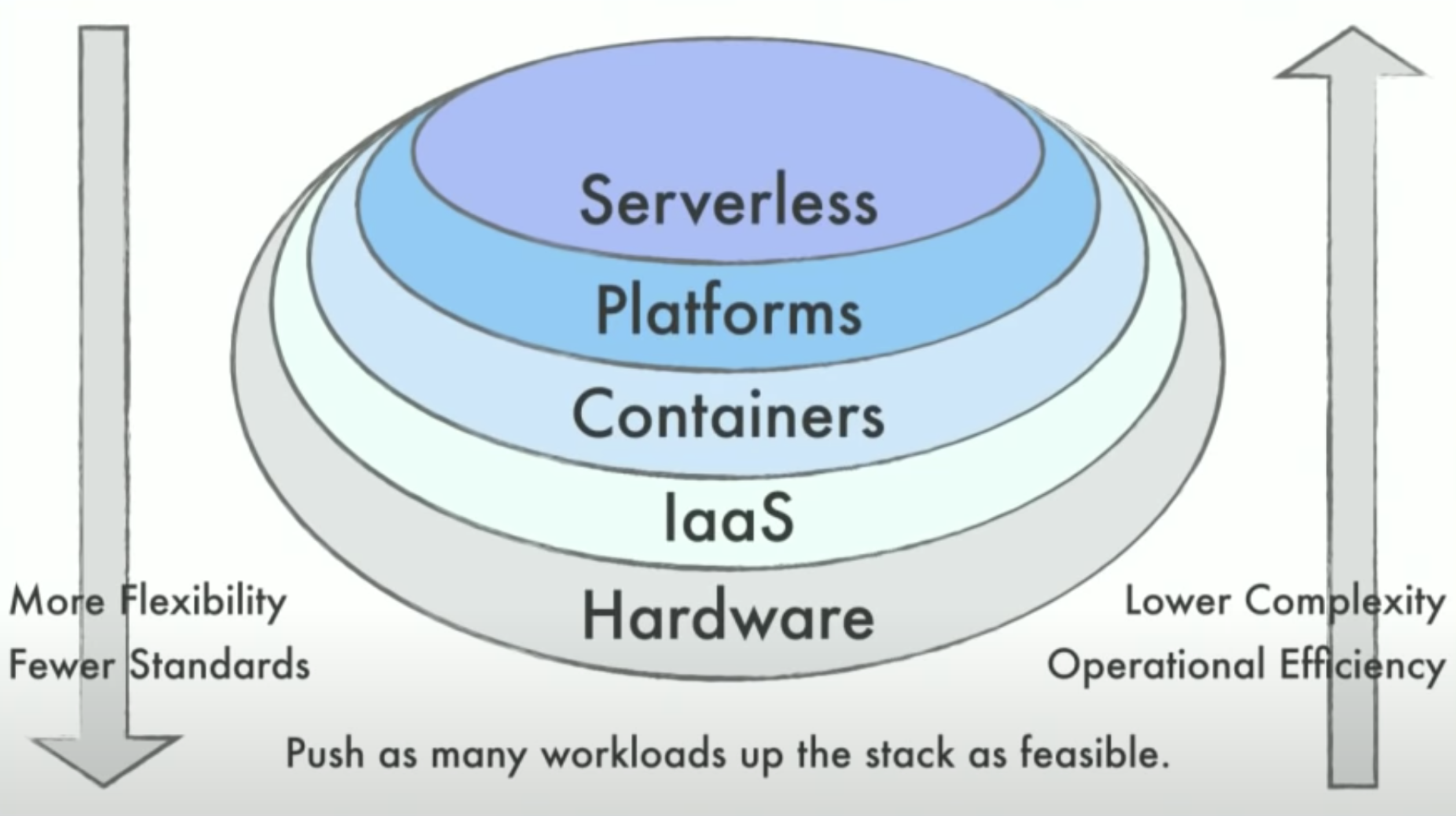
Different Levels of Services
Take a look at the below diagram to visualize solutions at different levels. At the lowest level (bare-metal), you are the most flexible since you got all the control over your system. However, you also have to deal with almost everything by yourself, including scaling, monitoring and, deployment. On the highest level (Serverless, FaaS), you can concentrate solely on writing your application. You give up some of the flexibility for more convenience.
Private Cloud
The Private Cloud is having a public cloud environment on the infrastructure that is dedicated to you.
That brings the disadvantage of being limited by your infrastructure’s limits and the advantage of having no other neighbors to share your resources.
Virtual Private Cloud
A Virtual Private Cloud is where a public cloud’s resources are divided into virtually isolated divisions - “private clouds”.
Isolating each division from each other creates the illusion of customers have their private cloud - but it’s only there virtually. Virtual Private Clouds are similar to virtual machines where there are no actual physical machines but only the isolation of resources.
Virtual Private Clouds are a type of Hybrid Clouds. Virtual Private Clouds are a type of Hybrid Clouds.
An Analogy
Imagine the public cloud as an internet cafe where they have these computers and charge you for the time you use them. In that case, the internet cafe is the vendor (in real life, this could be Amazon, Google, Microsoft, etc.). When you go and there and ask for a computer, they start your session on one of the available computers in the public area with others, using the same underlying infrastructure.
The private gaming rooms, in which they provide you an isolated internet connection from the ones in the public area and the other private gaming rooms. These rooms can be an analogy for virtual private clouds.
Let’s say this internet cafe vendor provides you the service to build one of these private gaming rooms at your house. They use your house’s infrastructure but with their computers and all the software in it. That would be the equivalent of a private cloud.
References
- https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/overview/what-are-private-public-hybrid-clouds/
- https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/cloud/what-is-a-public-cloud/
- https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/cloud/what-is-a-virtual-private-cloud/
- https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/cloud-computing/what-is-public-cloud
- https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/cloud-computing/public-cloud-vs-private-cloud-and-hybrid-cloud
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8tOj4A7jgWg